JIRA to DuckDB Bot: A Simple Python Data Pipeline with DLThub
Organizations often use JIRA for project management, and the need to automate data extraction from JIRA for analytics is common.
Senthilnathan Karuppaiah
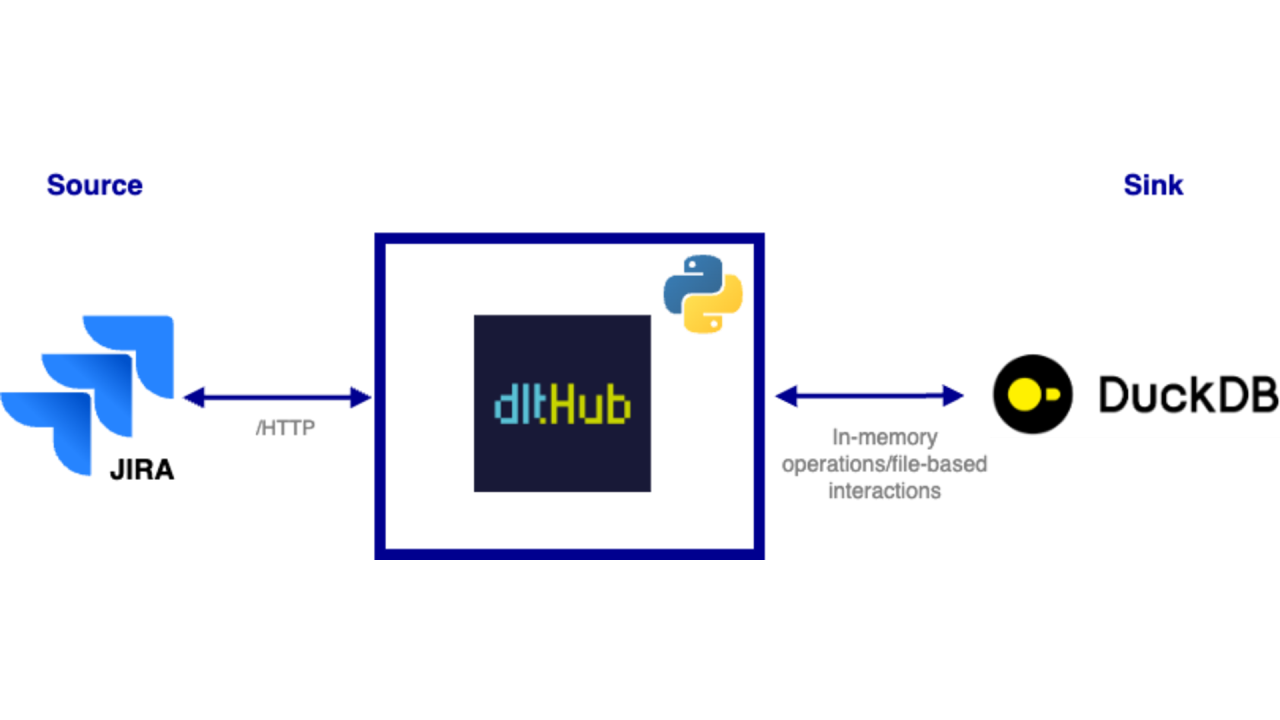
Use Case
Organizations often use JIRA for project management, and the need to automate data extraction from JIRA for analytics is common. The approach was to create a lightweight bot that automates the extraction of JIRA issue data using a JQL query, processes it in CSV format, and loads it into databases like DuckDB for development purposes or Snowflake for production-level analytics. This provides a streamlined and efficient solution for integrating JIRA data into an analytics pipeline.
This article serves as the foundation for a series of new articles focused on engineering metrics, covering how to collect, analyze, and visualize data to gain actionable insights enabling deeper reporting and better decision-making for engineering projects.
Design
Built as a bot using the Single Responsibility Principle (SRP), ensuring the process is modular and contained in a single Python file. Here’s a breakdown:
::list{type="success"}
- Environment Variables (.env): Key configurations like JIRA credentials, JQL queries, and the database sink are stored in environment variables, making it easy to switch between different environments without changing the code.
- Swappable Sinks: With DLThub, switching between development (DuckDB) and production databases (Snowflake) is seamless—just modify the configuration file and install the required packages.
- Lightweight & Embeddable: The bot is small and efficient, designed to avoid bulky dependencies, and runs in any environment (Jupyter Notebook or as a standalone Python script).
- Structured Logging: Using structlog, the bot logs all activities, making monitoring and debugging simple and effective. ::
Technology Stack
::list{type="success"}
- DLT (Data Load Tool): Powers the pipeline, handling data extraction and loading.
- DuckDB/Motherduck: Provides a fast, lightweight SQL database for development and small data lakes.
- Python: The language driving the automation and orchestration. ::
Folder structure
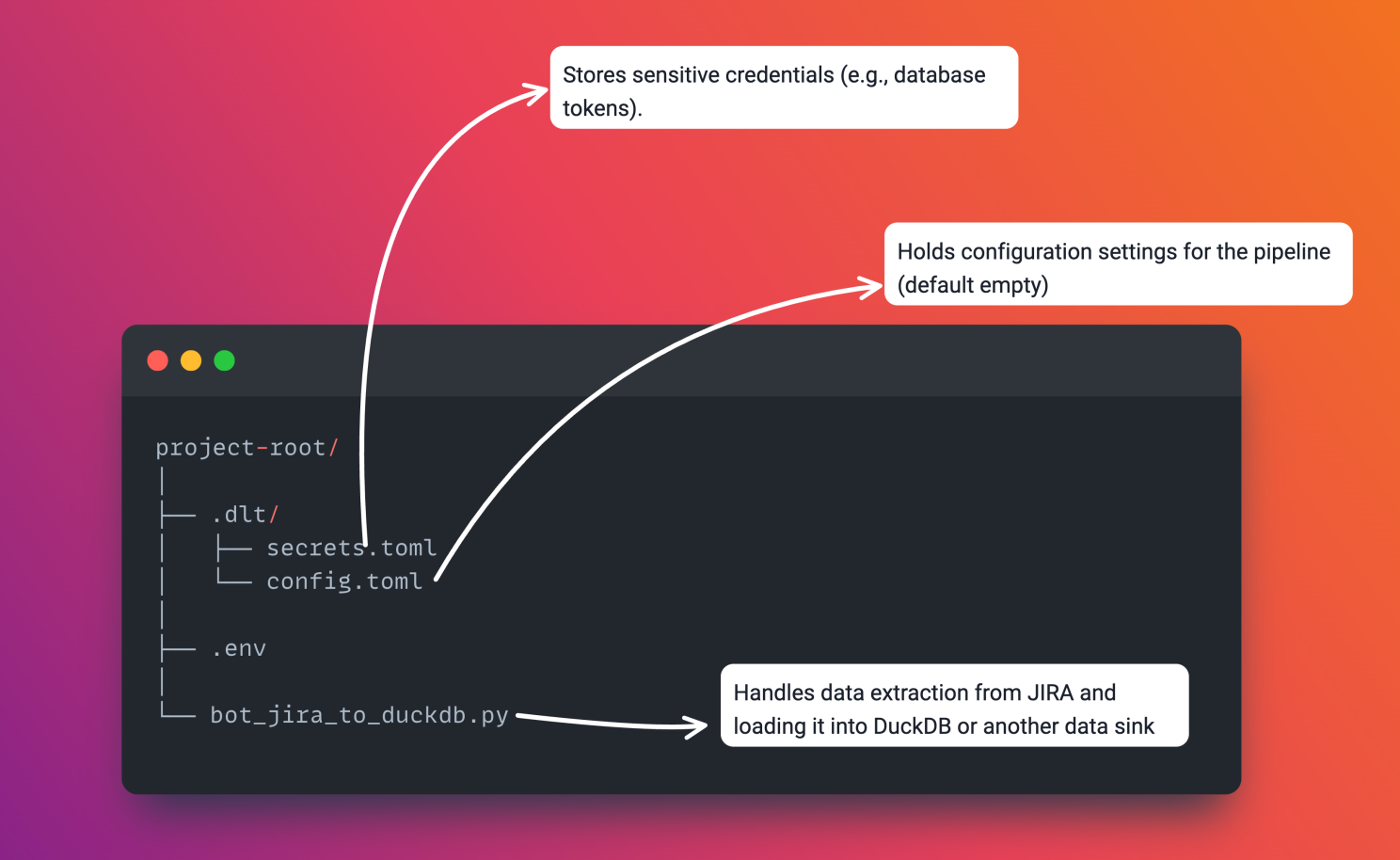
Prerequisites
::list{type="success"}
- Python Virtual Environment
- JIRA API Token and Username ::
Source Code
::list{type="success"}
-
[https://gist.github.com/senthilsweb/1e1caa0c9d95b3772c36d3a210caab11]
-
.env
JIRA_BASE_URL="https://yourdomain.atlassian.net/sr/jira.issueviews:searchrequest-csv-all-fields/temp/SearchRequest.csv"
JIRA_JQL='project = "GTMS" ORDER BY created ASC'
JIRA_AUTH_TOKEN="your_auth_token"
JIRA_USER_NAME="your_jira_email"
DLT_PIPELINE_NAME=templrjs #Duckdb filename
DLT_DESTINATION=duckdb # database type i.e. duckdb | motherduck | postgres
DLT_DATASET_NAME=pmo #schema name
DLT_TABLE_NAME=jira_issues # table name
- .dlt/secrets.toml (Optional as this example code doesn't require it)
[destination.motherduck.credentials]
database = "your_db"
password = "your_motherduck_token"
[destination.postgres.credentials]
database = "postgres"
username = "your_username"
password = "password" # replace with your password
host = "localhost" # or the IP address location of your database
port = 5432
connect_timeout = 15
Execute the Code to See the Results
python ./bot_jira_to_duckdb.py
Once you execute the script, it will create a DuckDB database file named temprjs.duckdb in the root.